Last updated 9/05/00
Trigonometry works on all triangles with a right (90°) angle in them. We call these triangles right-triangles.

There are 3 basic functions in the trig that we will be using: SINE, COSINE, and TANGENT. These functions can be applied to all angles in a right triangle. Each function represents a specific ratio between two of the triangle's sides.
The triangle's labeled sides correspond to a specific angle(q) -pronounced theta.
The ratio of sides in relation to a given angle is less than one for the sine and cosine functions. The functions and their ratios are

![]() = The degree
measure of the angle.
= The degree
measure of the angle.
Here is a word to help remember the relationships.
![]()
The sides of the triangle are defined as shown below
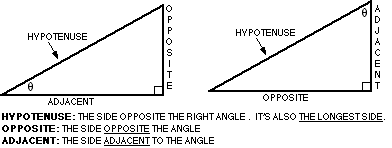
To interpret the trig relationships you would say that the
SINe of the angle ![]() is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the angle,
is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the angle,
![]() , divided by the
length of the hypotenuse. COSine
of
, divided by the
length of the hypotenuse. COSine
of ![]() is adjacent
relative to the angle,
is adjacent
relative to the angle, ![]() ,
divided by hypotenuse and TANgent
of
,
divided by hypotenuse and TANgent
of ![]() is opposite
divided by adjacent. Enough theory. Now for some examples. Make
sure your calculator is in the
degree mode because the
angle is in degrees.
is opposite
divided by adjacent. Enough theory. Now for some examples. Make
sure your calculator is in the
degree mode because the
angle is in degrees.
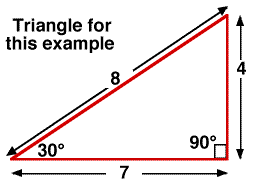
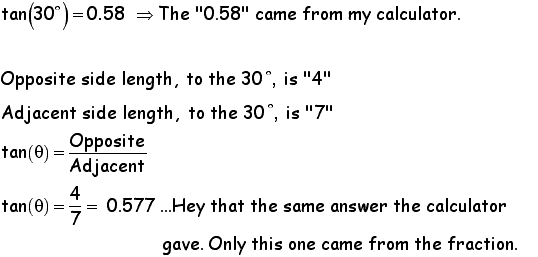


ANOTHER EXAMPLE
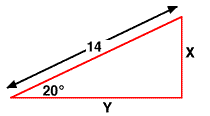
Given the triangle below find the length of the short side
(x).
SOLUTION
List all that you are given relative to the shown angle.
In this case the shown angle is the 20û angle.
- Opposite to the 20û angle is the unknown short side, "x."
- Adjacent to the 20û angle is another side of unknown length, "Y."
- The hypotenuse is given to be 14 units long.
Ask yourself, "Which function has the unknown (the opposite side), the angle, and the hypotenuse?"

The length of the short side is
4.8 units.
BELOW IS HOW TO USE YOU CALCULATOR'S TRIG FUNCTIONS TO FIND "X." EACH BLOCK REPRESENTS THE ACTUAL KEY YOU WOULD PUNCH TO GET THE ANSWER.
The display will show the answer of 4.788282007.
If the calculator shows 12.78123351 or 4.326237921 then it is in the wrong mode. It should be in the "DEG" or normal mode.
There are two ways to find the third side of the triangle. (1) use Pythagorean's Theorem or use a different trig with a function. To decide which one to use, use the one with the lowest probability of error. Since Pythagorean's Theorem uses an answer that was calculated, do not use it. (The previous answer may have been mis-calculated). Use a trig function that also does not use the previously calculated answer. Look at the unknowns and the given quantities above and decide which function to use. Do it now.
After looking you should have chosen COS.
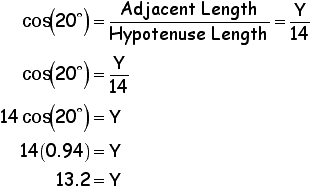
Therefore the length of the long side is 13.2 units.
FIND THE MISSING ANGLE MEASUREMENTS FOR THE TRIANGLE BELOW.
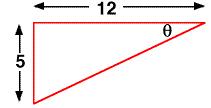
Start with finding the angle ![]() .
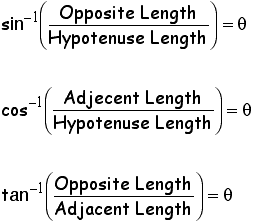
To do this, use an inverse-trig function. These functions are
symbolized as
.
To do this, use an inverse-trig function. These functions are
symbolized as
Relative to the angle we are given the opposite and adjacent sides. These givens suggests to use the TAN function.
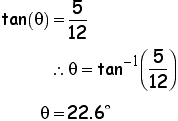

SOLUTION
The sides given relative to the angle ,q, are the hypotenuse and the opposite side. This suggests the use of the SIN function.

BELOW IS HOW TO USE YOU CALCULATOR'S TRIG FUNCTIONS TO FIND "O," THE ANGLE. EACH BLOCK REPRESENTS THE ACTUAL KEY YOU WOULD PUNCH TO GET THE ANSWER.
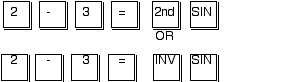
Which method you use depends on the calculator you use.
The display will show the answer of 41.81031489.
If the calculator shows 0.729727656 or 46.45590544 then it is in the wrong mode. It should be in the "DEG" or normal mode.
